Investor Account Access
Investor access to Shareowner accounts and Closed End Funds accounts.

Through various sponsor firms, Amundi US offers model-delivery SMAs as well as single- and dual-contract SMAs through a diverse range of actively managed equity and fixed income strategies. By leveraging our comprehensive reporting, reconciliation and portfolio management services, financial professionals can fully focus on helping clients craft the SMA portfolio that meets their needs.
Amundi US acts as a discretionary investment manager or non-discretionary model provider in a variety of separately managed account or wrap fee programs (each, an “SMA Program”) sponsored by a third party investment adviser, broker-dealer or other financial services firm (a “Sponsor”).
Amundi provides retail, institutional and corporate clients with innovative investment strategies and solutions tailored to their targeted outcomes and risk profiles.
| $2.286 tn |
|
66 |
| A top-10 global asset manager1 with $2.286 trillion AuM2 |
Convictions-driven, active-management approach and a broad suite of differentiated strategies to meet investor needs |
A global customer base covering 66 countries2 |
1Source: IPE "Top 500 asset managers" published in June 2023 and based on AUM as at December 2022
2Source: Amundi, as of March 31, 2024
3Amundi US is not affiliated with the data providers listed.
4Diversification does not ensure a profit or protect against loss.
†Source: Amundi, as of December 31, 2023.
The flexible structure of an SMA is designed to offer the investor the benefits of direct security ownership combined with the advantages of professional management.
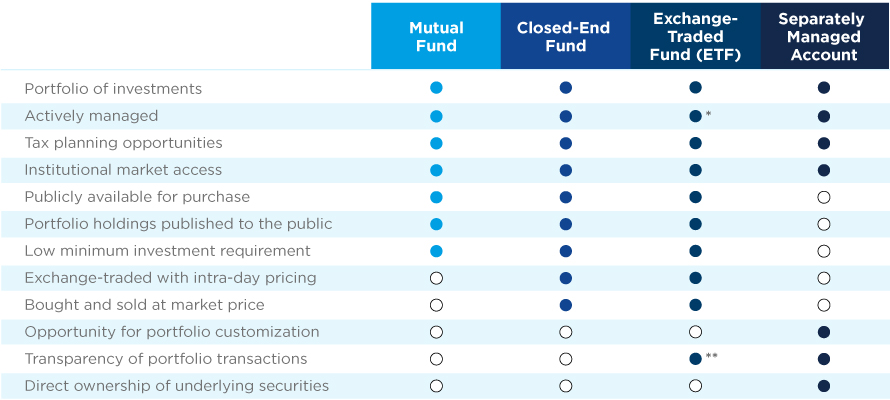
Mutual Funds, Closed End Funds, and ETFs are offered by a Broker-Dealer, while SMAs are offered by an Investment Adviser.
*ETFs and mutual funds can be actively or passively managed.
**Portfolio holdings are updated daily; shielded ETFs can disclose a proxy model.
Through our SMA strategies, Amundi US seeks to mitigate long-term risk by integrating our extensive investment expertise and research capabilities into active, fundamentally driven investment processes.
For more information, contact your financial professional.
A Word About Risk
Pioneer Core Equity SMA 1,2,4
Pioneer Disciplined Growth SMA 1,2,4,7,8
Pioneer Disciplined Value SMA 1,2,4,7,8
Pioneer Dividend Equity SMA 1,2,4,6
Pioneer Equity Income SMA 1,2,4,6
Pioneer Fundamental Growth SMA 1,2,3,4
Pioneer Global Sustainable Equity ADR SMA 1,2,5,9,10,11
Pioneer Large Cap Core SMA 1,4,5
Pioneer SMA 1,4,5
Pioneer US Large Core Equity SMA 1,4,5
1. The market prices of securities may go up or down, sometimes rapidly or unpredictably, due to general market conditions, such as real or perceived adverse economic, political, or regulatory conditions, recessions, inflation, changes in interest or currency rates, lack of liquidity in the bond markets, the spread of infectious illness or other public health issues or adverse investor sentiment. 2. Investing in foreign and/or emerging markets securities involves risks relating to interest rates, currency exchange rates, economic and political conditions. 3. The portfolio invests in a limited number of securities and, as a result, the portfolio’s performance may be more volatile than the performance of other portfolios holding more securities. 4. At times, the portfolio’s investments may represent industries or industry sectors that are interrelated or have common risks, making it more susceptible to any economic, political, or regulatory developments or other risks affecting those industries and sectors. 5. The portfolio generally excludes corporate issuers that do not meet or exceed minimum ESG standards. Excluding specific issuers limits the universe of investments available to the portfolio, which may mean forgoing some investment opportunities available to portfolios without similar ESG standards. 6. The portfolio invests in REIT securities, the value of which can fall for a variety of reasons, such as declines in rental income, fluctuating interest rates, poor property management, environmental liabilities, uninsured damage, increased competition, or changes in real estate tax laws. 7. The portfolio may invest in fewer than 40 securities, and as a result, the portfolio’s performance may be more volatile than the performance of portfolios holding more securities. 8. Investing in small and mid-sized companies may offer the potential for higher returns, but are also subject to greater short-term price fluctuations than larger, more established companies. 9. The portfolio is subject to currency risk, meaning that the Portfolio could experience losses based on changes in the exchange rate between non-US currencies and the US dollar. 10. The market price of securities may fluctuate when interest rates change. When interest rates rise, the prices of fixed income securities in the Portfolio will generally fall. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the prices of fixed income securities in the Portfolio will generally rise. 11. The Portfolio may use derivatives, which may have a potentially large impact on Portfolio performance.
Amundi US Equity ESG Improvers SMA
The market prices of securities may go up or down, sometimes rapidly or unpredictably, due to general market conditions, such as real or perceived adverse economic, political, or regulatory conditions, recessions, inflation, changes in interest or currency rates, lack of liquidity in the bond markets, the spread of infectious illness or other public health issues or adverse investor sentiment. The Portfolio generally excludes corporate issuers that do not meet or exceed minimum ESG standards. Excluding specific issuers limits the universe of investments available to the Portfolio, which may mean forgoing some investment opportunities available to funds without similar ESG standards. Investing in small- and mid-sized companies may offer the potential for higher returns, but are also subject to greater short-term price fluctuations than larger, more established companies. Some securities in which the Portfolio invests may have limited liquidity and, therefore, may be more difficult to purchase or sell; low trading volume may lead to market fluctuations that may impact the value of those securities. At times, the Portfolio’s investments may represent industries or sectors that are interrelated or have common risks, making it more susceptible to any economic, political, or other risks affecting those industries and sectors.
Important Information
Amundi US is the US business of Amundi Asset Management group of companies. Investment advisory services are offered through Amundi Asset Management US, Inc. Not all Amundi products and services are available in all jurisdictions.
The Amundi Asset Management logo used in this document only refers to a brand owned by Amundi and not to any service or product offered or manufactured by Amundi Asset Management SAS, headquartered in Paris. Amundi US acts as a discretionary investment manager or non-discretionary model provider in a variety of separately managed account or wrap fee programs (each, an “SMA Program”) sponsored by a third party investment adviser, broker-dealer or other financial services firm (a “Sponsor”). When acting as a discretionary investment manager, Amundi US is responsible for making and implementing all investment decisions in SMA Program accounts. When acting as a non-discretionary model provider, Amundi US’s responsibility is limited to providing investment recommendations (in the form of model portfolios) to the SMA Program Sponsor who may or may not, in their sole discretion, utilize such recommendations in connection with its management of SMA Program accounts. In such “model-based” SMA Programs (“Model-Based Programs”), it is the Sponsor, and not Amundi US, which serves as the investment manager to, and has trading responsibility for, the Model-Based Program accounts.
There is no guarantee that the portfolio will continue to hold any particular security and securities are held in varying percentages. Holdings are subject to change since the portfolio is actively managed. Holdings are intended to illustrate the composition and characteristics of the SMA for separately managed accounts. Across client portfolios, there may be variations in holdings, characteristics and performance information as dictated by reasons such as diversification needs, specific client guidelines, account size, cash flows, the timing and terms of execution of trades, and differing tax situations.
The Model Portfolio/SMA securities holdings information provided is intended solely for your use in evaluating the Model Portfolio/SMA portfolio(s). Under no circumstances does the information contained within constitute, and should not be construed as, investment advice, forecast of future events, a guarantee of future results, or a recommendation to buy, hold or sell securities.
Separately managed account programs may require a minimum asset level and, depending on specific investment objectives and financial position, may not be appropriate for all investors. Actual fees and account minimums may vary.
The investment strategies described are those of Amundi US. These materials are being provided for illustrative and informational purposes only. The information contained herein is obtained from multiple sources that are believed to be reliable. However, such information has not been verified, and may be different from the information included in documents and materials created by the sponsor firm in whose investment program a client participates. Some sponsor firms may require that these materials be preceded or accompanied by investment profiles or other documents or materials prepared by such sponsor firms, which will be provided upon request. For additional information, documents and/or materials, please speak to your Financial Professional or contact your sponsor firm.
Amundi Asset Management US, Inc
60 State Street, Boston, MA 02109
©2024 Amundi US
EXP-2025-02-21-ADID-3404016-1Y-T